Gouty Attack
Gout is one of the oldest diseases in medical history. It is a chronic disease occurring due to abnormal uric acid metabolism. This is a condition where excretion of the uric acid by the kidneys is reduced. Men are most vulnerable for Gout and about five percent of gouty patients are women; about 80% of them are post-menopausal at the time of onset.
When we consume protein, our body metabolism breaks it to form purine. Uric acid is a byproduct derived from purine. Normally our body excretes uric acid and other waste products through our kidneys; however, sometimes the kidneys fail to do the job and uric acid accumulates in blood and gets deposited in the joints of the body, kidney tissues.
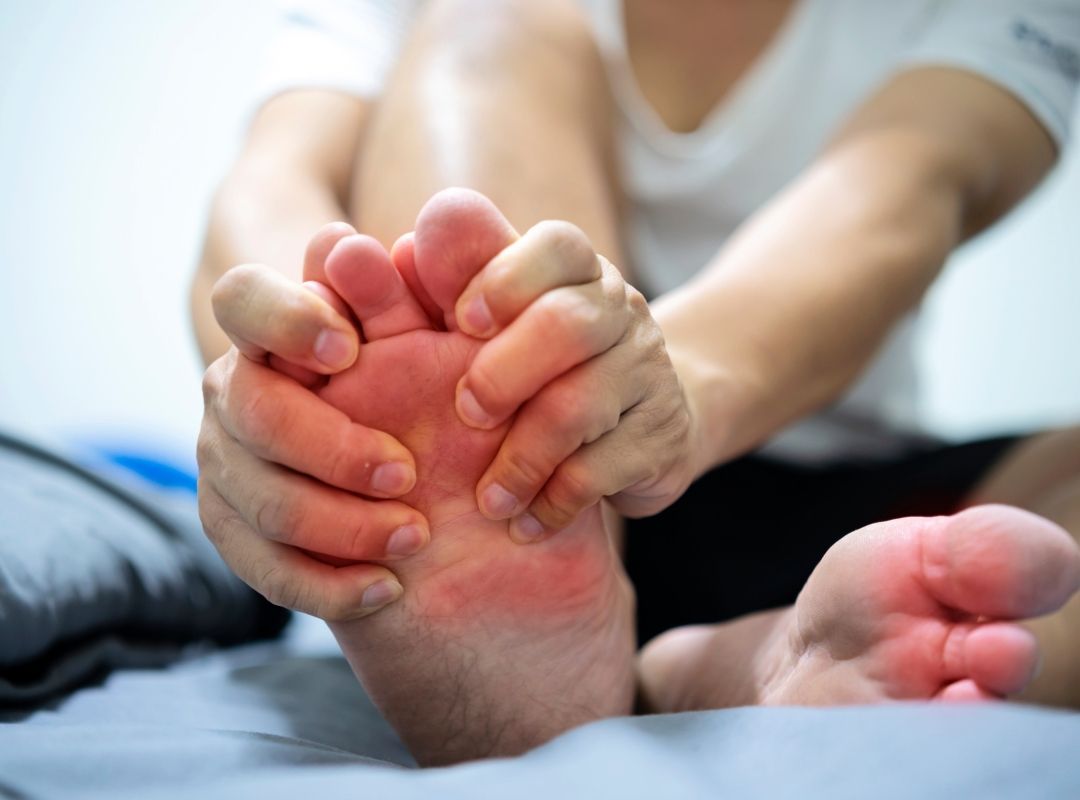
The joint where the great toe attaches to the foot is mostly affected and the bones of the middle of the foot, the ankle, the knee, the elbow and any joint can be affected.
If the levels of uric acids in your body increases, the levels of joint fluids also increases and when they become too rich in uric acid, crystals of this waste product begin to form in the fluid.
The formation of these crystals causes inflammation in the joint, which becomes red, swollen, and quite painful. The pain can be so extreme that you cannot even bear the weight of a bed sheet on the gouty joints. Such symptoms are known as gouty “attack”.
Deposition of uric acid and formation of this crystal also leads to kidney stone formation.
SERUM LEVEL
Uric acid estimation may be fallacious. It should be done in serum or plasma and not in whole blood. The normal upper limit of serum uric acid is 6 mg per 100 ml (357 Micromol /l) in men and 5 mg per 100 ml (297 Micromol/l) in women
About 200–500 mg (1.2–3) uric acid is derived from these sources in a person who eats animal food.
Causes and Risk Factors:
Abnormal uric acid metabolism: Reduced excretion of uric acid by the kidneys.
Diet: Consuming foods high in purines, such as red meat, organ meat, seafood, and certain vegetables.
Obesity: Being overweight or obese increases the risk of gout.
Medications: Certain medications, such as diuretics and aspirin, can interfere with uric acid excretion.
Symptoms:
- Gouty attack: Sudden, severe pain, swelling, and redness in the joints.
- Kidney stone formation: Deposition of uric acid crystals in the kidneys.
Prevention and Management:
- Fluid intake: Increasing fluid intake to 2-3 liters/day to help excrete uric acid.
- Dietary changes: Avoiding foods high in purines, reducing fat intake, and maintaining a healthy weight.
- Avoiding triggers: Avoiding alcohol, caffeinated beverages, and fructose-sweetened foods and drinks.
- Medications: Modifying drug therapy to minimize interference with uric acid excretion.
Importance of Awareness:
Understanding gout and its risk factors can help individuals take proactive steps to manage the condition and prevent complications.
Regular monitoring of uric acid levels and kidney function can help identify potential issues early.
By understanding gout and its causes, individuals can take steps to manage the condition and prevent complications.
NURTITIONAL CARE IN REDUCING URIC ACID LEVELS
- Fluid intake should be increased up to 2- 3 liters/day as it helps in excreting uric acid from the body and to prevent kidney stone.
- Stay away from High protein weight loss programs as it will multiply the risks of Gout.
- Obese people are more prone to gout, so they should try to reduce & achieve the Ideal Body Weight. Even 5-7 kg weight loss also can reduce your Gout risk up to 50 %.
- However, a rapid reduction of weight can raise blood levels of uric acid and provoke gout.
- Avoid starvation by Skipping meals and following crash diet as it can increase the blood uric acid levels.
- Avoid high fat cooking foods including fried Foods and creams.
- Alcohol drinks contain high level of purines. Hence Whisky, beer and red wine should be avoided which can lead to kidney stone formation.
- Caffeinated beverages can also increase the production of uric acid
- Fructose in the form of sweetened candies, cookies or soft drinks can also increases\ the production of uric acid
- High protein, low carbohydrate diets should be avoided since these diets encourages the formation of ketones that hamper the body’s ability to excrete uric acids.
- Diet should be low in fats as a high fat diet being high in its caloric content leads to weight gain & reduces the normal excretion of uric acid.
- Foods such as red meat, organ meat, sea food lentils, beans asparagus, mushrooms, sardines, and peas increases your risk of gout attacks because they contain high amounts of purines.
- Modify your drug therapy. Drugs like aspirin or diuretics for high blood pressure and pain-relieving medicines can interfere with normal kidney function and elimination of uric acid.
- Gout patients also may have hypertension, heart diseases, diabetes, and high blood cholesterol because gout can trigger ongoing inflammation in the body, and inflammatory compounds may also increase risk of blood clots. So, well balance meal is very important with good quality of foods.